All you need to know about website speed optimization is gathered here: causes, fixes and all. Let’s look at 10 ways to optimize a slow-loading website.
1 out of 4 web visitors tends to leave a website that takes more than 4 seconds to load. Thus today’s crowd of internet users is notorious for their short attention spans, and that is bad news for website publishers whose pages are not up to optimum speed.
Until a website is in a prim and proper state, there’s 46% of the online crowd who’d altogether avoid visiting these poorly performing sites.
Moreover, there’s already a high risk of cart abandonments, which in 2022 is up to 70%, and that is irrespective of the website performance. So, to steer away from such high abandonment rates and miss out on potential conversions, you need to ensure your website is up to speed and in its prime shape.

Points to Be Covered
- Too Many Elements on One Page
- Heavy Plugins
- Excessive Number of Ads
- Media File Sizes Affecting Speed
- Speed Affected Due to Geographic Locations
- The Bandwidth isn’t Large Enough
- Overloading of HTTP Requests
- Unsatisfactory Server
- Stagnation Caused by Unoptimized JavaScript
- Appropriate Use of Caching
Here are 10 Causes & Fixes to Try for a Slow-Loading Website
Your website may be slowing down due to several reasons, some of these being – high traffic; too many images and plugins; code not being up to date; poor performance of server; due to location; absence of caching, and so on.
Also Check: Website Monetisation for Publishers: Techniques
And to help you with that, here below, we’ll discuss the 10 popular fixes for issues that often lead to websites loading slowly.
Page Elements
It is not just the size of media files that can affect the website loading time, but also the number. Too many media files can cause the website code to bloat and lead to slower speeds. More than half of web users agree that they’d rather have faster websites than videos or animations.
But does that mean you should sacrifice all the heavy media files altogether? Compromise is key. Maintain a balance between too little and congested, and you should be good to go. First, do away with the unnecessary media elements.
If you’re unsure about what to do away with, you can take the help of the heat map test, which shows which media files are showing higher engagement. You can then do away with the poor-performing ones. And, if you see your website is still performing poorly, with only the absolute necessary media elements. You can then alter their sizes.
In addition to managing media files, staying updated with the latest web design trends is crucial to prevent slow-loading websites, as outdated design practices can inadvertently increase loading times.
Web Plugins
While plugins may seem convenient, having too many of them can result in poor website speed. They can be as simple as your social media page-sharing plugins.
Every plugin needs to retrieve data from their respective sites, thus causing the host website to slow down.
First, try to replace the bulky plugins with lighter ones, and do away with all the unnecessary plugins. Secondly, you can try and use tools online, which help in assessing the plugins that are causing the poor performance of the website.
For social media sites, you can keep only the main plugins, say for Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter, or whichever platforms are performing the best.
Number of Ads
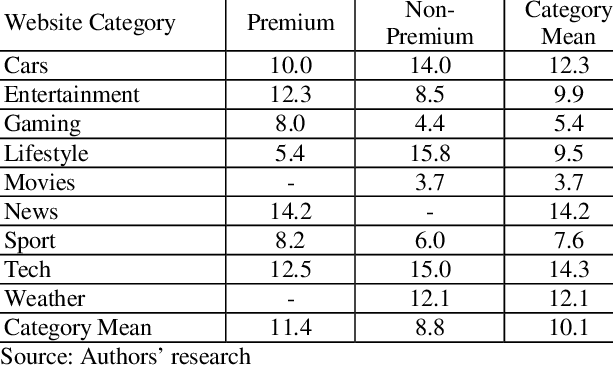
(Source: Researchgate.net)
Like images, videos, and content, ads take up space on your website and can be the reason why your website is slow, especially if you’re hosting third parties to advertise on your website.
Too many ads not only lengthen the time it takes for pages to load but also end up frustrating your viewers. You end up losing valuable clients who are worth much more than the money you’d generate from advertisers, which is also getting affected due to the bounce rates.
If ads are your primary source of revenue, then having too many is costing you money. Your focus should be on getting quality advertisers and not more on quantity. Keep it limited to one or two ads per page. This will keep your page loaded somewhat rapidly and draw more users to your website.
Also Read: Tackling 5 Biggest Ad-Blocking Myths That Might be Hindering Your Growth
Media File Sizes Affecting Speed
Websites need to be visually appealing to engage the user, which demands publishers to add images and videos. This, however, also leads to slow loading of websites when these files are large, perhaps without description or an alt tag, and overall unoptimized.
Moreover, web engine like Google doesn’t recognize your media files until they come with a description or an alt tag. So what can you do?
Your first step would be to resize your images and make sure you keep the ratio intact. Then with the help of the plethora of tools available online, compress the media files to lesser sizes. Next would be to alter your images to .jpg and .png file extensions. Opt for the former on regular, and go for the latter only if your image requires intricate details, for instance, the logo of a website.
For videos, optimizing them to a limited size can be tricky. So, what you can do is host the videos through an external platform, say YouTube, and then embed the video onto the page.
Website Speed Affected Due to Geographic Locations
If you’re hosting a website from one corner of the world, it is obvious that the website won’t run at a similar speed everywhere. Website speeds can differ in separate geographic locations, and to tackle that, web hosts employ a CDN.
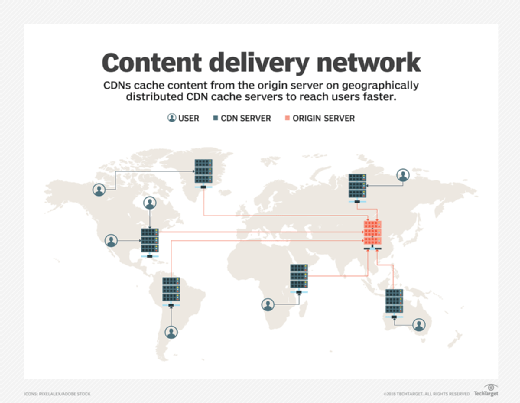
A CDN or a Content Delivery Network’s job is to serve a website to a user from a location that is close to them. The shorter distance ensures higher speeds. The CDN acts as a buffer between the server and the user, making sure the data doesn’t have to travel a long distance.
There are platforms available online that can help with this task and deploy a CDN to ensure a streamlined and efficient delivery all across the world. Thus, users from Australia can load the same website at a similar speed as can users from Afghanistan or Austria.
Also Check: Geotargeting vs. Geofencing: Differences Explained
The Bandwith Plan
The goal for a website owner is to maintain steady high traffic. However, too many visitors to a website can easily topple a website, causing it to malfunction. This is a common problem faced by websites, which tend to stop working when the traffic gets a little higher than it can handle.
Well, this can be very easily sorted out. All you need to do is to contact the site’s host and increase your bandwidth plan. Bandwidth translates to the tenacity or the capacity of an internet connection in terms of handling information at a given time.
HTTP Requests
Instilling a high number of image, CSS, and JavaScript files into your website can cause an excessive number of HTTP requests. The moment a user tries to access your website, the web browser makes multiple requests to load each of these files leading to a considerable slowing down of the page load time.
One way to tackle this issue is to reduce HTTP requests by using sprites. And as discussed before, you can lessen the number of files on your pages, as and where applicable. This includes Javascript, CSS, and other media files.
Web Server
If you’re racking your head over trying to find out the issue with your website speed, it may just be the issue is with the ISP or the server itself when a user tries to access the website, the browser pings up the server asking for the data and information to be loaded. When this takes longer than usual, it simply means the problem lies with the engine itself.
Cheap web hosts or service providers may seem exciting, but they usually offer shared servers, thus affecting your website performance in the long run. So, it is best not to compromise your website performance and opt for a reliable web host.
Stagnation Caused by Unoptimized JavaScript
JavaScript can save a website as much as cripple it. While JavaScript can ensure your website is not dull, help you add enough dynamic elements, and create a fun and interactive medium between your users. If it’s not up to date, it can also detriment your website speed and performance.
How this works is that when a web browser tries to open a page or a website, it has first to load all the code and then display the page. The unoptimized JavaScript code prevents the page from loading quickly, leading to website abandonment. Thankfully, there are multiple approaches you can take to this problem.
- Edit the code to its optimal shape and cut out the unnecessary or extra elements, as heavy code will lead to delayed website speed.
- Use inline JavaScript and replace the external JavaScript files.
- Instil asynchronous loading, ensuring that your webpage and the code load separately.
- Delay the loading of the code altogether until after the webpage has loaded.
Appropriate Use of Caching
Caching is likely one of the most crucial steps to site speed optimization. The act of caching involves keeping a copy of your website’s files in a location which is known as a web cache.
Without caching, the client’s browser repeatedly requests for your website’s assets i.e. the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript elements, from your originating server rather than utilizing the local or intermediary cache. Servers can only handle a certain number of requests at once, and the absence of cache layers results in the queuing of the requests, in turn causing slower loading of the websites.
To deal with this, you can take the help of the HTTP headers, which allow you to control the caching policy for your website. Through the configuration of your web server, you can change them. You can also take the help of a content delivery network that applies to this issue as well. And most importantly, there’s a wide assortment of caching plugins available online for you to automate the process.
Wrapping Up!
While today’s internet users may be on the move and expect rapid loading of websites, slowing down of websites is a common problem every publisher has to face.
Hopefully, the problems and fixes discussed above will be of help to you, as these are more than often the reason behind poorly performing websites. Keep everything up to date and optimized, try out the fixes, and you should have a website at its prime!
FAQ
The ideal website loading time, whether for desktops or mobiles, shouldn’t be more than 4 seconds. 2-4 seconds is deemed perfect. More than that, and you may be losing your consumers.
Your website may be loading fine on your server and not on another’s. One way to check your website’s performance is to take the help of the Analytics tools online or perform a survey with the help of Google PageSpeed insights and other relevant technology.

Shubham is a digital marketer with rich experience working in the advertisement technology industry. He has vast experience in the programmatic industry, driving business strategy and scaling functions including but not limited to growth and marketing, Operations, process optimization, and Sales.

![CTV vs OTT Advertising: Which one is Right Pick for Publishers? + [6 Bonus Strategies] Ott vs Ctv](png/featured-image-270x180.png)


