As the internet is continuing to expand and online video and streaming are become more prevalent, choosing the correct video file format has become essential for publishers to ensure their content is compatible with various platforms and devices.
Gone are the days where video players were known only for performing basic operations such as streaming video content and ad hosting. But, nowadays, video players have advanced functionalities, and support the following features:
- Video players control the workflow of video ads and architecture of video content.
- Provide better insights, analytics to the publishers.
- Offer video ad monetization opportunities that help publishers to generate revenue to their video content.
Publishers investing in video players see 25-35% higher RPM than publishers who don’t use a video player. So, if you are you thinking about monetizing with video advertising, you’re on the right track to choose the best video player for your website.
However, with hundreds of available options for choosing the best video players, it is best to choose a player that can run in-stream ads, outstream ads, and support different video file formats available.
See here: Best Video Players for Publishers
That said, we will today explore the top 10 video file formats for 2023 that are best suited for online video and streaming, along with their advantages and disadvantages.
We’ll also provide tips and guidelines for choosing the correct video file format for your needs and best practices for optimizing the use of video file formats.
So, let’s get started!
Top Video File Formats for Publishers
Let’s first look at the different types of video file formats. including their features and compatibility.
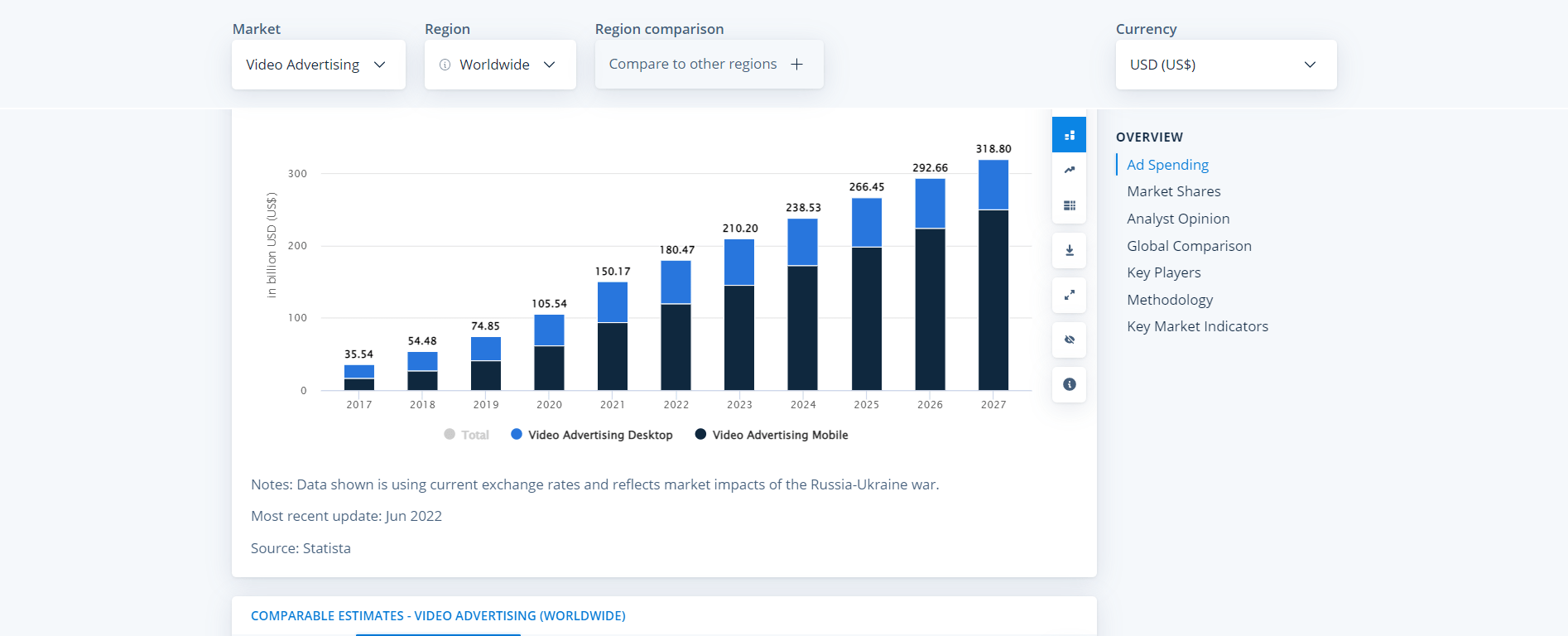
(Also Check: Video ad spending for the USA region 2017-2027.)
1) MP4 (MPEG-4 Part 14)
MP4 is a popular video file format known for its high compression rate and ability to maintain high-quality video with small file sizes. It’s compatible with most devices and platforms, making it a versatile online video and streaming option.
2) AVI (Audio Video Interleave)
AVI is an older video file format that’s still commonly used, especially in Windows operating systems. It supports multiple codecs, making it a flexible option for different types of video content.
3) MOV (QuickTime Movie)
MOV is a video file format developed by Apple and used primarily on Mac operating systems. It’s compatible with QuickTime, making it a popular choice for video editing software.
4) WMV (Windows Media Video)
WMV is a video file format developed by Microsoft and used primarily on Windows operating systems. It’s known for its high compression rate and compatibility with Windows Media Player.
5) FLV (Flash Video)
FLV is a video file format used primarily for online video and streaming, mainly on Adobe Flash Player websites. It’s known for its ability to maintain high-quality video with small file sizes.
6) WebM
WebM is an open-source video file format developed by Google and designed specifically for online video and streaming. It’s compatible with most web browsers and supports high-quality video with small file sizes.
7) MPEG-2 (Moving Picture Experts Group 2)
MPEG-2 is a video file format used primarily for digital television and DVD video. It supports high-quality video and multiple audio streams, making it a popular choice for commercial video content.
8) DivX
DivX is a video file format known for its high compression rate and compatibility with various devices and platforms. It’s famous for both online video and streaming and offline video playback.
9) H.264 (Advanced Video Coding)
H.264 is a video file format known for its high-quality video and small file sizes. It’s compatible with most devices and platforms and is commonly used for online video and streaming.
10) HEVC (High-Efficiency Video Coding)
HEVC is a video file format that maintains high-quality video with even smaller file sizes than H.264. It’s still gaining popularity but quickly becoming a popular choice for online video and streaming.
Check Here: Top 7 Ad Networks with the Best Video Advertising Formats
Advantages and Disadvantages of Top 10 Video File Formats
Now that we understand the different video file formats available let’s examine their advantages and disadvantages. We’ve ranked these formats based on compatibility, compression rate, and quality.
MP4 (MPEG-4 Part 14)
Advantages
- High compression rate without sacrificing video quality
- Compatible with most devices and platforms
- Supports a wide range of codecs
Disadvantages
- Limited support for advanced features such as 3D video
WebM
Advantages
- Open-source and royalty-free
- Optimized for online video and streaming
- Supports high-quality video with small file sizes
Disadvantages
- Limited compatibility with some devices and platforms
- H.264 (Advanced Video Coding)
Advantages
- High-quality video with small file sizes
- Compatible with most devices and platforms
- Widely used for online video and streaming
Disadvantages
- Limited support for advanced features such as 3D video
AV1 (AOMedia Video 1)
Advantages
- Open-source and royalty-free
- Supports high-quality video with small file sizes
- Designed specifically for online video and streaming
Disadvantages
Limited compatibility with some devices and platforms
HEVC (High-Efficiency Video Coding)
Advantages
- Maintains high-quality video with even smaller file sizes than H.264
- Compatible with most devices and platforms
Disadvantages
- Limited support for older devices and platforms
- Higher processing power is required for encoding and decoding
MPEG-DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP)
Advantages
- Adaptive streaming for improved user experience
- Compatible with most devices and platforms
Disadvantages
- More complex to implement than other formats
- Limited support for some older devices and platforms
VP9 (WebM Project)
Advantages
- High-quality video with small file sizes
- Open-source and royalty-free
- Widely used for online video and streaming
Disadvantages
- Limited compatibility with some devices and platforms
AVI (Audio Video Interleave)
Advantages
- Supports multiple codecs and video resolutions
- Compatible with most devices and platforms
Disadvantages
- Large file sizes compared to other formats
- Limited support for advanced features such as 3D video
- QuickTime (MOV)
Advantages
- High-quality video with a wide range of codecs
- Compatible with Mac operating systems
Disadvantages
- Limited compatibility with non-Mac devices and platforms
FLV (Flash Video)
Advantages
- Supports high-quality video with small file sizes
- Widely used for online video and streaming
Disadvantages
- Limited compatibility with some devices and platforms
- Flash Player is no longer supported on some browsers
Read More: The Complete Guide to Video Ad Monetization: Everything You Need to Know
What Should You Consider While Picking the Best Video File Formats?
When choosing a video file format, several factors must be considered, including quality, size, compatibility, and ease of use.
Quality
The quality of a video format refers to how good it looks and sounds. Higher-quality video formats produce better-looking images, smoother motion, and richer colors. The main factors that affect video quality are resolution, frame rate, and color depth.
Resolution
Resolution is the amount of pixels in numbers in a video image. Higher resolutions produce sharper and more detailed photos. The most common online video and streaming solutions are 720p, 1080p, and 4K.
Frame Rate
This refers to the number of video frames per second. Higher frame rates produce smoother motion and reduce motion blur. The most common frame rates for online video and streaming are 24fps, 30fps, and 60fps.
Color Depth
It refers to the number of colors a video can display. Higher color depths produce richer and more accurate colors. The most common color depths for online video and streaming are 8-bit and 10-bit.
Size
The size of a video file refers to how much storage space it takes and how long it takes to download or stream. Smaller video files are more accessible to store and stream but may sacrifice quality or features. The main factors that affect video size are compression, bit rate, and file container.
Compression
This refers to reducing the size of a video file by removing redundant or unnecessary data. Compression can be lossless or lossy. Lossless compression preserves all the original data but produces larger files, while lossy compression sacrifices some data to make smaller files.
Bit Rate
This refers to the data used to represent each second of the video. Higher bit rates produce the higher-quality video but larger files. The most common bit rates for online video and streaming are 2-10 Mbps.
File Container
This refers to the format used to store video and audio data in a single file. Different file containers have different features and compatibility with different devices and platforms. The most common file containers for online video and streaming are MP4, WebM, and AVI.
Compatibility
The compatibility of a video format refers to how well it works with different devices, browsers, and operating systems. Some video formats may require specific codecs or plugins to play on certain devices or platforms. The main factors that affect video compatibility are codecs, DRM, and streaming protocols.
Codecs
This refers to the software that compresses and decompresses video data. Different codecs have different compression algorithms and quality levels. The most common video codecs for online video and streaming are H.264, H.265, and VP9.
DRM
DRM refers to the digital rights management used to protect copyrighted video content. Different DRM systems have different levels of security and compatibility with different devices and platforms. The most common DRM systems for online video and streaming are Widevine, FairPlay, and PlayReady.
Streaming Protocols
This refers to the method used to deliver video over the internet. Different streaming protocols have different features and compatibility with different devices and networks. The most common streaming protocols for online video and streaming are HTTP Live Streaming (HLS), Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH), and Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP).
Best Practices for Using Video File Formats
Now that we have covered the top video file formats for 2023 and their respective advantages and disadvantages, it’s essential to know how to optimize the use of these formats.
Here are some best practices and tips for using video file formats:
Encoding
Choose the appropriate encoding settings based on the intended use of the video. For example, if the video is designed for streaming, use a format optimized for streaming, such as H.264.
Compression
Compress video files to reduce their size without sacrificing quality. It can be done using software or online tools. Be careful to compress the video sparingly, as this can result in a loss of quality.
Resolution
Choose the appropriate resolution based on the intended use of the video. Higher-resolution videos are more suitable for larger screens or presentations, while lower-resolution videos are more suitable for mobile devices or email.
Bitrate
Choose the appropriate bitrate based on the intended use of the video. Higher bitrates result in better-quality videos and larger file sizes, while lower bitrates result in smaller file sizes but lower-quality videos.
Testing
Test the video file format on different devices and platforms to ensure compatibility and optimal viewing experience.
Also Read: IABs Video Ad Standards: Everything You Need to Know
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with the best practices in place, you may need help using video file formats. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting tips to help you resolve them:
Playback Issues
If your video is not playing correctly, try updating your media player or using a different media player. Check the video file format if the problem persists to ensure it matches your media player.
Compatibility Issues
If your video is incompatible with a particular device or platform, try converting it to a consistent file format. There are several software programs and online tools available that can help you convert video file formats.
Formatting Errors
If you receive an error message when trying to play or upload your video, check the video file format and ensure it is correctly formatted. Some common formatting errors include incorrect frame rates or aspect ratios.
Encoding Issues
If your video is taking too long to encode or the encoding process fails, check the encoding settings and ensure they are optimized for the intended use of the video. Try encoding the video using a different software program or online tool.
Ready to Earn More Revenue?
Choosing the right video file format is crucial for optimizing online video and streaming in 2023.
After analyzing the top 10 video file formats, we recommend using the H.265 or HEVC format for its high-quality video with a smaller file size and broad compatibility.
AdPushup provides high-impact ad formats and helps publishers create video ad monetization strategy that drives performance and revenue. To get help choosing the right video player for your publishing business and implementing it correctly, get started here.
FAQ
A video file format is a standardized way of encoding and compressing video data for storage or transmission. Examples of video file formats include MP4, AVI, and MOV.
Consider quality, size, compatibility, and intended use when choosing a video file format. It’s essential to select a widely supported design that can be played on various devices and platforms.
In 2023, the H.265 or HEVC video file format is recommended for online video and streaming due to its high-quality video with a smaller file size and broad compatibility.
To optimize your use of video file formats, follow best practices such as encoding, compression, and resolution settings. It’s also important to consider your video content’s intended use and target audience.
If you encounter playback or compatibility issues with a video file format, try troubleshooting steps such as updating software, adjusting settings, or converting the file to a different format.

Shubham is a digital marketer with rich experience working in the advertisement technology industry. He has vast experience in the programmatic industry, driving business strategy and scaling functions including but not limited to growth and marketing, Operations, process optimization, and Sales.