Organic traffic is the holy grail that every web publisher desires. It brings engaged users to your website, who are considered valuable by advertisers.
Both publishers and advertisers benefit from organic traffic. But getting a constant and ever-increasing supply of organic traffic remains a challenge.
Webmasters try various techniques like search engine optimization, link building, and others to increase their traffic. All of this starts with finding the right keywords. Keyword optimization is the next step.
What is Keyword Optimization?
Keyword optimization is the process of researching, analyzing, and using keywords to drive relevant traffic. It covers both organic and paid searches.
The basic idea behind keyword optimization is to find words and phrases (long-tail keywords) frequently searched by users. Using these, you can create content that answers the questions users are searching for.
By keeping keyword optimization as an on-going activity, you can keep discovering new keywords and create a database of existing and potential keywords. This helps devise a strategy that continues to bring relevant and quality traffic to your website.
Why Publishers Need Keyword Optimization
As per HubSpot research, organic search traffic accounts for 94% of all web traffic. Also, the first search result on Google has 34% CTR for desktop and 35% CTR for mobile. Basically, your content needs to reach not just the first page, but also the first position to compete better. But how would you reach there? By doing keyword optimization.
No matter the size or niche, you need to have a strategy that gets constant organic traffic. Unfortunately, most publishers do not put much time and effort into keyword optimization simply because they find it tedious.
However, in order to be found on search engines, one needs to ace the keyword game. You might already be creating quality content, but, to appear on the first page, keyword optimization is as important as quality content.
If we talk about digital publishers, their traffic brings them impressions and hence ad revenue to their pockets. To keep the revenue coming, publishers need to ensure non-stop production of quality content and continuous keyword optimization.
Furthermore, to measure the value of their inventory, publishers need to know the keywords they are already ranking for. In the world of CPC, some keywords pay more than the others. Hence, knowing such details can help them make more money.
Understanding Types of Keywords
Short tail keywords: The simplest types of keywords containing not more than two words. These generally have a huge monthly volume and are used as parent keyword in an SEO strategy. For example, ‘Lipstick’ can be the parent keyword for a beauty blogger’s SEO plan.
Long-tail keywords: Keywords having more than two words are categorized as long-tail keywords. Long-tail keywords (phrases) have comparatively less volume. But they also have less competition, increasing your chances to rank for them. Continuing with the same example, given that ‘lipstick’ may be the parent keyword of a beauty blogger’s keyword plan; a more specific search query like ‘buy red matte lipstick’ would be the long-tail version of it.
Trending keywords: These keywords depend on the news of your niche or industry; or something that has hyped or become a buzzword recently. Here is an example:
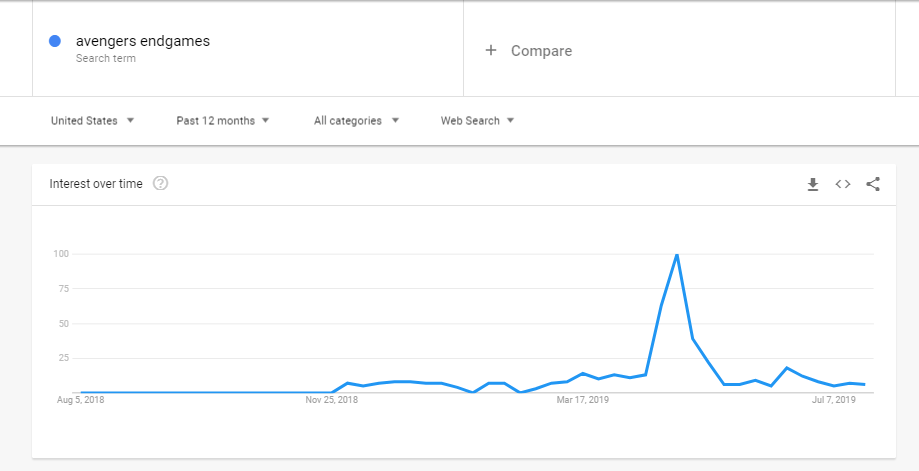
You can see the volume for the search term ‘avengers endgame’ got a significant hike in the month of April and May. This was around the time when the movie was released. However, the search term saw a sharp drop after that. Therefore, we can say that at their peak, trending keywords are likely to bring good traffic.
Evergreen keywords: In contrast to trending keywords, evergreen keywords are the terms that users are always searching for. For example, ‘how to lose weight’ is a key-phrase that people all over the web would continue to search all year long. Covering such keywords, depending on your industry, can bring constant traffic.
LSI keywords: Latent Semantic Indexing refers to the terms that appear as the subtopic for your main keyword. For example, if your main keyword is ‘header bidding’, you would also want to cover ‘what is header bidding’, ‘advantages of header bidding’, ‘how does header bidding work’, and others. The purpose of using LSI keywords is to cover all the topics searched by users similar to your main keyword to create a well-structured and detailed post for a better search ranking.
Finding Keywords That Work
Keyword optimization starts with keyword research. Meaning, you need to find keywords that are likely to attract users to your website.
Cover The Basics First
Suppose a publisher writes about financial investment articles and news to educate users on how to better invest their money. Such publishers would want to start with basic questions their users would want to know—like types of investments, how to invest in mutual funds, etc. Chances are that there is already a lot of existing content covering these keywords, so you have to top them by providing more value in terms of better content. So, think like a user and try to cover as many “how-tos” and “what is” as you find.
1. Don’t Forget to Add Long Tail Keywords
50% search queries are four words or longer. Users are typing phrases intoto the search box, they have queries and questions. Short keywords like “blue shoes” would have immense competition (for both organic and paid traffic). In such a case, you would want to go for long-tail keywords like “blue shoes under $50 for men”. As mentioned earlier, long-tail keywords have less competition and increase your chances of showing up at the top of search results.
2. Look What Competitors are Doing
Along with the list of keywords, you must also prepare a list of your competitors who target a similar audience. Find out the keywords/keyphrases that they are ranking for and use those for your keyword strategy. Competitor research can save you when you don’t have much time to spare for keyword research.
3. Take Help of Online Tools
There are a plethora of SEO tools that offer great help. Here are some well-known tools that can help you with keyword research:
- Keywords Everywhere: It offers a browser extension for monthly search volume, CPC, and competition. The extension is available for Google Chrome and Firefox browsers. It shows real-time search volume of keywords you search along with a list of similar keywords to improve your LSI targeting. Keywords Everywhere takes help of Google Keyword Planner to generate its data and show it to you.
- Alexa Keyword Matrix: This is a paid feature by Alexa that takes in the details of your competitors and evaluates your competitors to tell you about the keywords that you are missing on your site. This tool also helps in creating an exhaustive SEO plan by providing keyword clusters based on competitor matrix.
- SEMrush Keyword Research: This tool does a really nice job to evaluate your site based on your niche and shows you potential keywords you didn’t know before. It also offers competitor analysis to get keywords your competitors are ranking for.
- Ahrefs Keywords Explorer: This is one of the most extensive tools for keyword research. A single search brings about hundreds of similar results. Along with the volume, you get to see keyword difficulty metrics, SERP results, trends, clicks, CPC, parent keyword, etc to frame your SEO strategy accordingly.
- KWFinder: It is a rather simpler keyword research tool compared to others. It provides a user-friendly dashboard to check keyword data including monthly volume, difficulty, and other deep insights.
Invest Time in On-page SEO
But before you publish it on your site, make sure the post is well optimized and search engine friendly. Here is how you can do it:
- Title of the post: Title is something that will make a user click the link and read on. It has to be eye-catchy and informative at the same time to get users interested. Make sure you use the keyword in the title and make a good title out of it.
- Use appropriate images: The content in an image is never scanned by the search engine crawlers. Hence, it will not directly affect SEO ranking. But adding images makes the content easier to understand for readers. And adding alt text can make the image rank in case of an image search for the keyword.
- Meta description: Each content has to be published with a snippet to give a quick description of the content that you are posting. This helps users understand what your post is about and also let search engines rank it.
- URL of the posts: While publishing a post, you can optimize a part of URL called slug. A well-structured slug containing the keyword(s) can help the search engine recognize the content on the web. Ideally, you should use keyword in slug but keep it descriptive as well.
- Internal and outbound link: Search engines love nicely linked content. For that, you need to add links to your own website (other blog topics) and external sites like data sources. Well-linked content is awarded with higher rankings on search engines.
In Closing
Nothing can magically increase your organic seo traffic. Put time to understand your audience and study their requirements to design content that informs, educates, and answers.
Never get involved in unethical SEO practices, otherwise, search engines like Google will penalize you for that. Try to keep a record of your niche keywords and competitors list handy. Competitor analysis can help you on dry days when you are out of keywords and content ideas.
Finally, make sure any strategy you put into action is not causing inconvenience to the users in any way. If we talk about the keywords, black-hat SEO practice and keyword stuffing are major offenses.
Every time you follow these tips, you create an optimized piece of content for both search engines and readers. So next time you wish to work on your organic traffic, use these guidelines to bolster your existing strategy.

Shubham is a digital marketer with rich experience working in the advertisement technology industry. He has vast experience in the programmatic industry, driving business strategy and scaling functions including but not limited to growth and marketing, Operations, process optimization, and Sales.